Industry Trends
Social Media

Written By
Karen Bryant
Social Media Director
As artificial intelligence continues to take the world by storm, and with new tools and integrations evolving at unprecedented speed, it’s easy to see that AI is not going anywhere anytime soon. In fact, it’s reshaping whole industries, and the social media landscape, like everything else in marketing, will be affected.
AI tools such as Anyword AI, Rytr and Copy.ai promise social media teams more engaging content with automated performance forecasts. ChatGPT — which continues to dominate many of the headlines about AI — takes on the role of brainstorming bestie, outlining content calendars, providing answers and generating scratch work at the click of a button.
While ChatGPT is a jack-of-all-trades, some tools operate under a social-first approach, with enhanced social media marketing features that differentiate them. Meanwhile, others simply offer social integrations, supporting a larger interface. Whatever your need, there is probably an AI tool that at least purports to provide a solution.
However, while AI is surely changing the social media world, it’s not going to flip it on its head. Why?
The humanness of social media is what made it attractive in the first place.
At its core, organic social media is all about building relationships and fostering connections. It’s where brands come to tell their stories and get to know their respective audiences by creating a sense of community and helping them along their journey through thoughtful interactions. According to a Q1 2023 pulse survey conducted by Sprout Social, marketers rank organic social above paid social advertising as the most impactful social media tactic. It’s no doubt the humanness of organic social media holds substantial value in the marketing world — value that can’t be disrupted by AI.
Consider:
No one, including AI technology, can understand your brand, product or target audience better than you, the human.
The human element of organic social media — which is a fundamental part of the channel’s appeal — cannot be replaced.
*sighs in relief*
Alas, while lines get blurred and AI weaves its way into our work at Wray Ward, we’re analyzing how we can maximize efficiency and minimize risk when using AI tools for organic social media with a three-pronged approach: Content Creation, Community Management, and Analytics and Performance. For each, we’re breaking down how AI can support these tactics with “how can” questions and caveats that demonstrate how AI cannot walk through the door without a human holding its hand.
Let’s dive right in.
Content Creation
How can AI help brainstorm and write calendars?
Whether we’re gearing up to write five weeks of posts adapted across channels or knitting a unique campaign into evergreen, “always on” content pieces, content creation requires planning, support and timeliness. Consider these reasons integrating AI into this work is attractive:
Automated and efficient content generation: Large language models can generate both short-form and long-form social media content at scale, as we know. But they can also add automation to content scheduling through optimal post time suggestions, hashtag help and more.
Brainstorming and ideation help: AI helps create detailed content outlines, kick-starting the content creation process and speeding up the brain power it takes to get content off the ground faster.
Personalized content recommendations: Large language models, or LLMs — when given sufficient guidance and content cues — are able to tailor messaging to key target segments and can create different versions of content to test across audiences and social channels.
Efficiency and scale of work created? Yes. Something to rely on word for word, without careful review and revisions? Not quite.
What’s the catch?
While AI tools can be great conceptualizing partners, they fall short in replicating real, authentic voices. With that, overreliance on such tools can create problems in maintaining originality, accuracy and creativity on social media platforms.
AI relies heavily on the human gatekeeper to contribute technical brand and product knowledge and ensure accuracy. The information we want to get out of AI is only going to be as good as the prompts and keywords we give it. The question then becomes, “How do you talk to an AI machine to get you what you want?” Shared best practices for optimal prompts and keywords are vital in ensuring accuracy, because the AI tool will absorb what we say as fact.
It’s up to us as social writers to be in the driver’s seat, as well as to know our specific engaged audience and what will drive the best engagement — leading us right into …
Community Management
How can AI-powered assistants help support customers?
Brands are always going to have customer service issues, and the more brands grow, the more customers turn to social media for their questions and inquiries. Here are a few use cases where AI can help address and categorize these issues:
Around-the-clock automation and issue identification: While humans are off the clock, chatbots and virtual assistants are available 24/7, promptly fielding questions and monitoring response times.
Proactive engagement: AI can work behind the scenes to identify audience members who consistently react and engage with content, prompting community managers to build deeper relationships with such users.
Routine FAQ inquiries: With a mix of pre-written responses and template suggestions, AI helps cut down on busy day-to-day work, so the community managers can handle the more hefty inquiries.
Sentiment analysis: With automated positive, negative or neutral assignments, AI adapted for social works to identify areas for improvement or concern.
Yes, but …
The importance of human-to-human connection goes beyond the comment section. When relying on AI tools to connect with an audience, we lose the ability to create a catered connection with the user asking the question or making the inquiry. Plus, users may start to lose trust if they don’t feel seen or heard on the platform at hand.
When it comes to sentiment analysis, it’s important to consider the context of the conversation between parties on a given platform before passing the baton to AI to make the determination.
Sprout Social recently introduced a new way for social media managers to categorize community management items as positive, negative or neutral (as pictured). Its built-in machine learning often selects the sentiment with the intent to make things easier when weeding through its Smart Inbox. However, machine learning, while advanced, is unable to identify indicators such as sarcasm or figures of speech, often leading to inaccurate sentiment scores and skewed data.
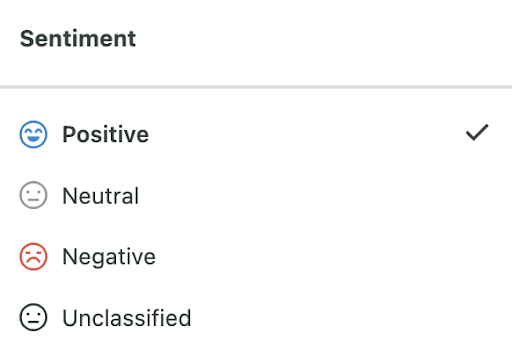
Source: Sprout Social
To account for this downfall, there has to be a human gatekeeper to keep things in check.
Analytics and Performance
How can AI-powered analytics help make data-driven decisions?
Reporting, data and insights are the bread and butter behind organic social media. We use them to draw takeaways to inform our social strategies and analyze trends, patterns and responses we see with the content we put out into the world.
Data gathering and visualization enhancements: As with copywriting, AI for social is enabled to compile and interpret large quantities of data in a fraction of the time it would take to complete the task manually.
Predictive and competitive analysis: Acting as an analysis assistant, AI can alert social media managers of emerging trends and topics to leverage in future content, gauge how target segments perceive the brand and products, and identify points of further differentiation based on competitor performance.
Synthesizing data information for reporting: To help refine strategies over time, AI tools can offer support with a detailed view of what’s working and what’s not. For example, AI could identify response patterns by compiling comments connected to a specific piece of content or campaign.
Proceed with caution.
Using AI tools to work with data can be a game changer, but conscious guidelines need to be in place when inputting any information into AI tools. When inputting data into an AI machine, the data then becomes vulnerable to misuse and potential unauthorized access.